Cách tính nguyên hàm phân thức
Dạng bài tập tính nguyên hàm của phân thức là dạng bài khá cơ bản mà các em học sinh được học ở môn Toán lớp 12.
Hàm phân thức có các công thức tính riêng, chỉ cần áp dụng là có thể làm được dạng bài này.
Công thức nguyên hàm phân thức
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Cách tính nguyên hàm phân thức
Bài tập 1. Cho ![]() . Khi đó tổng S = A + B + C bằng
. Khi đó tổng S = A + B + C bằng
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
Giải:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ Chọn đáp án B.
Ví dụ 2. Tìm ![]() là:
là:
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
Giải:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
⇒ Chọn đáp án B.
Bài tập 3. Cho ![]() . Khi đó
. Khi đó ![]() bằng:
bằng:
A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3
Giải:
![]()
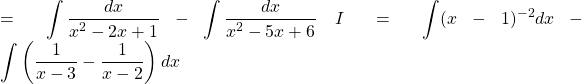
![]()
![]()
⇒ Chọn đáp án B.
Bài tập 4. Cho ![]() . Khi đó
. Khi đó ![]() bằng
bằng
A. 2 B. −2 C. 1 D. 0
Giải:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Suy ra ![]()
⇒ Chọn đáp án D.
Bài tập 5. Tìm hàm số f(x)= x2 + ax + ln |bx+ 1| + c biết ![]() và f(0) = 1. Khi đó S = (2a − b)3.c bằng
và f(0) = 1. Khi đó S = (2a − b)3.c bằng
A. 0
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. 4
Giải:
Ta có:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Mà ![]() nên
nên ![]() Khi dó,
Khi dó, ![]()
Suy ra ![]() nên
nên ![]()
